To reduce vertices in Blender, go to the “Edit Mode,” then select “Mesh,” and choose “Decimate” from the dropdown menu. Adjust the “Ratio” to reduce vertices while preserving the overall shape and details of the model.
Reducing vertices in Blender is a common need when working with complex 3D models. By using the “Decimate” tool, you can effectively decrease the vertex count without compromising the model’s quality. This process is particularly helpful for optimizing models for real-time applications or reducing file sizes for easier handling and sharing.
In this guide, we’ll explore the steps to reduce vertices in Blender, providing you with the knowledge to streamline your 3D modeling workflow and produce efficient, high-quality models.
Understanding Blender Model Optimization
Understanding Blender model optimization is crucial for creating efficient and high-performance 3D models. Optimizing Blender models involves reducing the number of vertices while maintaining the visual quality of the model. When you reduce vertices in Blender, you streamline your models, making them more optimized for rendering and real-time applications. Let’s delve into the details of understanding and implementing Blender model optimization.
Importance Of Optimizing Blender Models
Optimizing Blender models is essential for improving performance, reducing file size, and enhancing rendering speed. By reducing the number of vertices, your models become more efficient, allowing for smoother workflows and improved user experience. Additionally, optimized models are easier to work with, making it simpler to manipulate and edit them during the design process.
Effects Of Unoptimized Models
Unoptimized Blender models can lead to performance issues, longer rendering times, and increased file sizes. When models contain excessive vertices, it can strain system resources, causing lag and slowdowns during manipulation and rendering. Additionally, unoptimized models can hinder the overall project workflow, resulting in longer production times and potential compatibility issues when sharing or using the models in different applications.
Analyzing Performance Bottlenecks
When working with 3D models in Blender, performance bottlenecks can significantly impact your workflow. Analyzing performance bottlenecks involves identifying areas with a high vertex count and evaluating materials and textures for optimization opportunities.
Identifying High Vertex Count
In Blender, the number of vertices in a model can directly affect the performance. To identify areas with a high vertex count, select the object and go to the ‘Object Data’ tab in the Properties panel. Here, you can view the vertex count for the selected object, allowing you to pinpoint specific areas that may need optimization.
Evaluating Materials And Textures
Materials and textures play a crucial role in a 3D model’s performance. Examine the materials applied to your model and evaluate their complexity. Similarly, review the textures used, considering their resolution and compression. This evaluation will help identify opportunities to optimize materials and textures for improved performance.
Reducing Vertices In Blender Models
Learn how to efficiently reduce the number of vertices in your Blender models. This simple technique can help optimize your 3D models, improving performance without sacrificing quality. Mastering this method will enhance your workflow and lead to faster rendering times in Blender.
Reducing the number of vertices in Blender models is a crucial step in optimizing your 3D designs. The more vertices a model has, the more complex it becomes, which can lead to slower performance and larger file sizes. Fortunately, Blender provides several methods to simplify mesh geometry and reduce the number of vertices effectively.
Simplifying Mesh Geometry
One of the primary techniques for reducing vertices in Blender models is by simplifying the mesh geometry. This involves removing unnecessary detail while retaining the overall shape of the model. By simplifying the mesh, you can achieve smoother performance and make your file sizes more manageable.
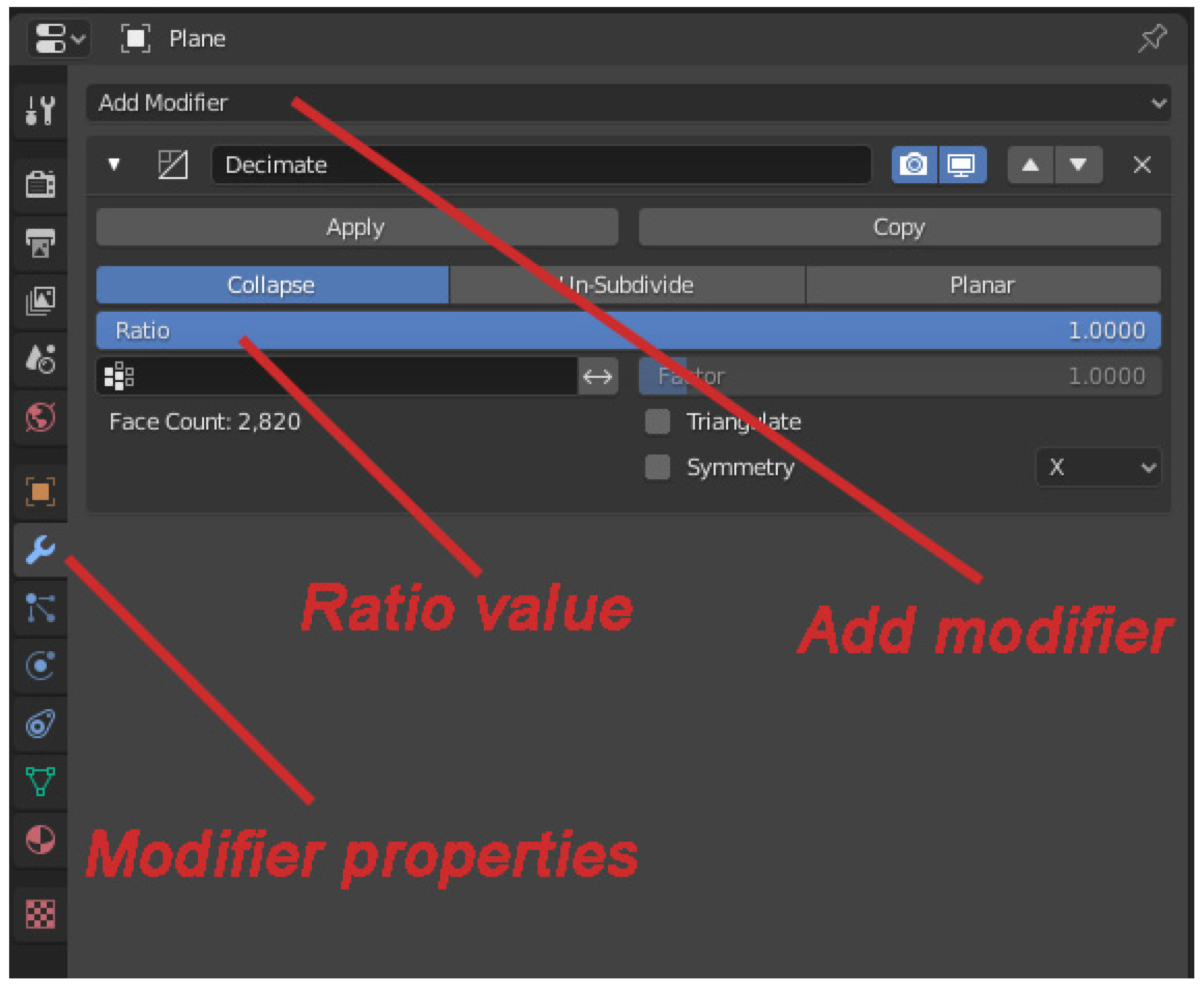
Using Decimate Modifier
One of the most straightforward ways to reduce vertices is by using the Decimate modifier in Blender. This modifier simplifies the model’s geometry by removing excess vertices based on various algorithms, such as Collapse and Un-Subdivide.
To use the Decimate modifier, follow these steps:
- Select your model in Blender.
- Open the Properties panel by pressing the ‘N’ key.
- Click on the ‘Modifiers’ tab.
- Click on the ‘Add Modifier’ button and select ‘Decimate’ from the menu.
- Experiment with different options available, such as ‘Collapse’ or ‘Un-Subdivide’, to find the best reduction method for your specific model.
- Adjust the ‘Ratio’ parameter to control the amount of vertex reduction. Higher values yield fewer vertices but may affect the model’s overall shape.
- Preview the changes by toggling the modifier on and off using the eye icon next to it.
- Once you are satisfied with the result, apply the modifier by clicking on the ‘Apply’ button.
Using the Decimate modifier is a flexible and efficient way to reduce vertices and optimize your Blender models. Remember, finding the right balance between simplicity and retaining the necessary level of detail is crucial to achieving the desired results.
By employing these techniques and making use of Blender’s powerful tools, you can effectively reduce vertices in your models without compromising their overall quality. Whether you are creating complex scenes or game assets, optimizing your geometry will enhance performance and streamline your workflow. So, try out these methods and unlock the full potential of your Blender designs.

Credit: www.jig.space
Streamlining Materials And Textures
Learn how to optimize your 3D models in Blender by reducing vertices, which can help streamline materials and textures. By using various techniques such as retopology and decimation, you can effectively simplify your models without compromising their overall appearance and quality.
When working with 3D models in Blender, reducing the number of vertices is crucial for optimizing performance and improving render times. One effective way to achieve this is by streamlining materials and textures. By managing texture resolution and consolidating material slots, you can drastically reduce the complexity of your models without sacrificing visual quality.
Managing Texture Resolution
Texture resolution refers to the level of detail in your textures. While high-resolution textures can provide intricate details, they also tend to have a higher number of pixels, which increases the number of vertices in your model. To reduce vertices, consider these tips for managing texture resolution:
- Use texture atlases: Instead of assigning separate textures to different parts of your model, combine them into a single image known as a texture atlas. This reduces the number of texture slots and optimizes memory usage.
- Downscale textures: Assess the resolution of your textures and determine if they can be safely downscaled without compromising visual quality. Aim for a balance between resolution and performance.
- Bake textures: If you’re using procedural or high-resolution textures, consider baking them onto UV maps. Baking transfers the texture details onto a simplified UV map, reducing the need for complex geometry.
Consolidating Material Slots
Material slots define the appearance of different parts of your model. While it’s tempting to assign separate materials to every element, this can quickly lead to a bloated model with an excessive number of vertices. To reduce vertices, follow these guidelines for consolidating material slots:
- Merge similar materials: If multiple materials share the same attributes and only differ in color or texture, consolidate them into a single material slot. This reduces the number of distinct materials used in your model.
- Utilize material nodes: Blender’s material node system allows you to create complex materials using a network of nodes. By using procedural textures and shader nodes, you can achieve a variety of visual effects without the need for additional material slots.
- Simplify material complexity: Evaluate the complexity of your materials and identify areas where simplification is possible. Removing unnecessary nodes and reducing shader complexity can significantly reduce the number of vertices in your model.
Optimizing Rendering Settings
Optimizing rendering settings in Blender is crucial for reducing vertices and achieving smooth and high-quality visuals. By making strategic adjustments to parameters like anti-aliasing and shadow quality and utilizing simplified lighting techniques, artists and 3D designers can optimize their renders and enhance the overall efficiency of their projects.
Adjusting Anti-aliasing
Anti-aliasing plays a significant role in reducing jagged edges or “jaggies” in rendered images. It smooths out these edges by sampling neighboring pixels and blending their colors. Adjusting the anti-aliasing settings in Blender can help optimize rendering without compromising on the visual quality. Here’s how:
- Identify the target level of smoothness. Determine how jagged you want your edges to appear. The higher the anti-aliasing level, the smoother the edges but also greater computational resources required.
- Access the Render tab. Click on the Render tab in the Properties panel of Blender.
- Locate the Sampling settings. Scroll down in the Render panel until you see the Sampling settings.
- Adjust the Anti-Aliasing setting. Increase or decrease the Anti-Aliasing value to achieve the desired level of smoothness. Higher values result in smoother edges but may increase render times.
Shadow Quality
Shadow quality can greatly impact the overall realism and performance of your renders. By adjusting the shadow settings in Blender, you can reduce the number of vertices used and improve the efficiency of your scenes. Consider the following steps:
- Assess the required level of shadow detail. Determine the desired level of shadow quality for your project. Higher quality shadows are more realistic but require more computational power.
- Navigate to the Shadows section. Scroll down in the Render panel to find the Shadows settings.
- Modify the Shadow Maps resolution. Increase or decrease the value of the Shadow Maps resolution depending on the desired level of shadow quality. Higher values improve quality but can impact render time and memory usage.
- Adjust the Soft size. Increase or decrease the Soft size to control the softness of the shadows. Higher values create softer shadows.
By carefully adjusting the anti-aliasing and shadow quality settings in Blender, you can achieve smoother edges and optimize the rendering process. Don’t hesitate to experiment with different values to strike the right balance between visual quality and render efficiency.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Testing And Validating Model Performance
In order to ensure that your 3D models in Blender are optimized for performance, it is crucial to test and validate their performance before finalizing your projects. By measuring render times and comparing performance metrics, you can identify and reduce the number of vertices in your models, leading to improved performance and a better overall user experience.
Measuring Render Times
To get accurate measurements of render times, you need to render your model and record the time it takes to complete the process. This will help you determine the efficiency of your model and identify any potential bottlenecks. To measure render times in Blender, follow these steps:
- Open your Blender project and navigate to the “Render” tab.
- Select a suitable rendering engine, such as Cycles or Eevee.
- Adjust any necessary settings, such as resolution or lighting.
- Click on the “Render” button and note down the time it takes to complete the rendering process.
By measuring render times, you can track the performance of your model over time and identify any areas where optimization is needed.
Comparing Performance Metrics
Along with measuring render times, it is essential to compare performance metrics to understand how your model stacks up against industry standards or previous iterations. By analyzing these metrics, you can identify areas where your model may be too complex and optimize it accordingly. Some essential performance metrics to consider include:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Vertex Count | The total number of vertices in your model. |
| Face Count | The total number of faces or polygons in your model. |
| Triangle Count | The total number of triangles in your model. |
| Texture Size | The dimensions and file size of your model’s textures. |
By comparing these performance metrics, you can identify any areas of concern, such as models with an excessive number of vertices or large texture sizes that may impact performance. This information can then be used to modify your models and reduce vertices, ensuring optimal performance.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Reduce Vertices In Blender
How Can I Reduce Vertices In Blender?
Vertices reduction can be achieved in Blender by using the Decimate modifier. This modifier allows you to reduce the number of vertices in your mesh while preserving the overall shape and structure. Simply add the Decimate modifier to your object and adjust the Ratio value to control the level of vertex reduction.
What Is The Purpose Of Reducing Vertices In Blender?
Reducing vertices in Blender can help optimize your model by reducing its file size and improving its performance. It can also make your mesh easier to work with, especially when it comes to modifying and sculpting. By reducing unnecessary vertices, you can achieve a more streamlined and efficient 3D model.
Are There Any Downsides To Reducing Vertices In Blender?
While reducing vertices can be beneficial, it’s important to note that it can also lead to some drawbacks. Excessive vertex reduction can result in loss of detail and distortion in your model. It’s crucial to strike a balance between reducing vertices and maintaining the overall quality and accuracy of your 3D mesh.
Can I Selectively Reduce Vertices In Blender?
Yes, you can selectively reduce vertices in Blender by using various tools and techniques. For example, you can manually delete specific vertices that are not essential to your model’s overall shape. Another option is to utilize the Dissolve Vertices feature, which allows you to remove unnecessary vertices while preserving the overall topology of your mesh.
Conclusion
Reducing vertices in Blender is a crucial skill for creating efficient 3D models. By following the tips and techniques discussed in this blog post, you can optimize your models for better performance and faster rendering. Remember to analyze the complexity of your mesh, utilize modifiers, and use tools like decimation and simplification to effectively reduce vertices without compromising the quality of your models.
Start implementing these strategies today and take your Blender creations to the next level.
